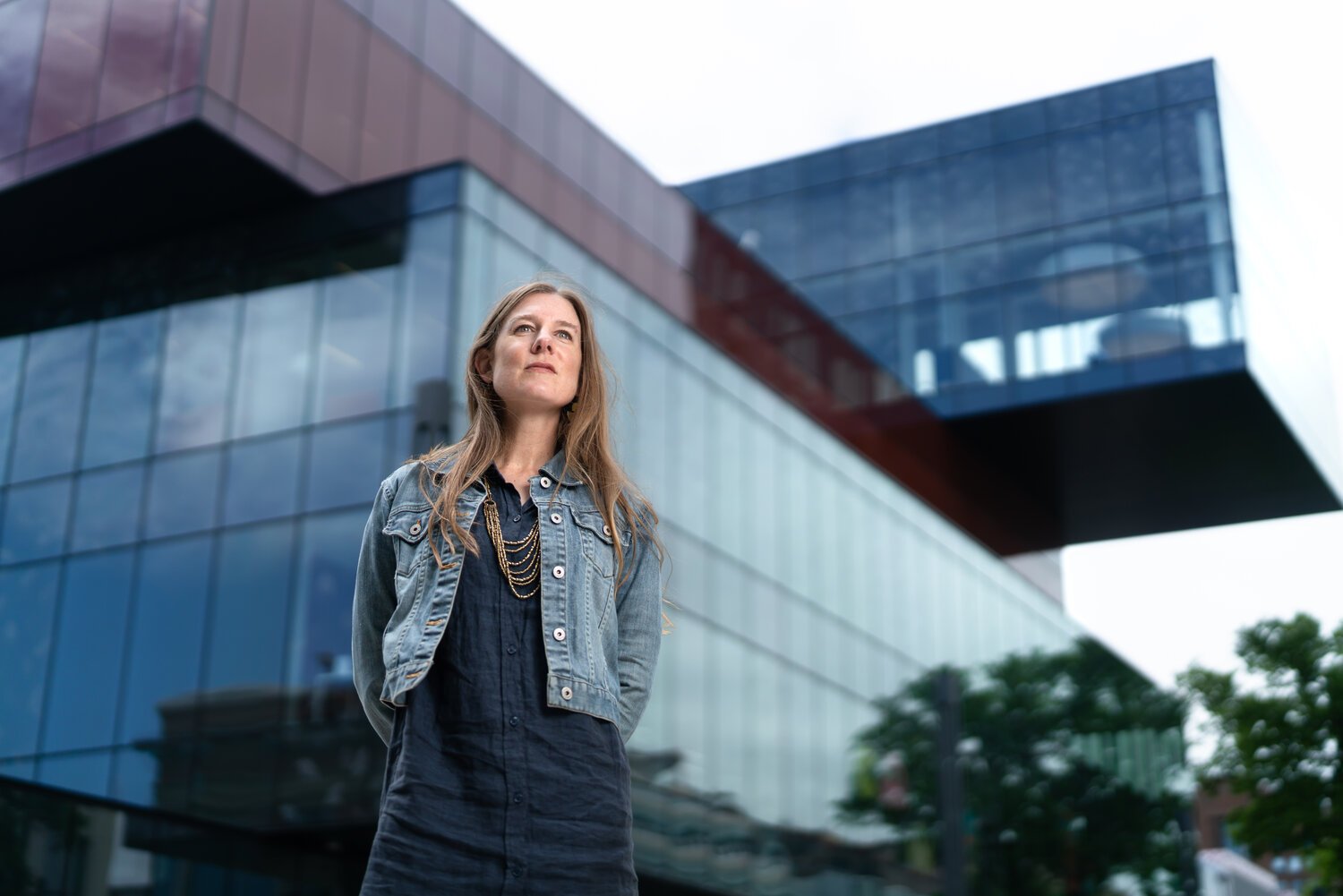
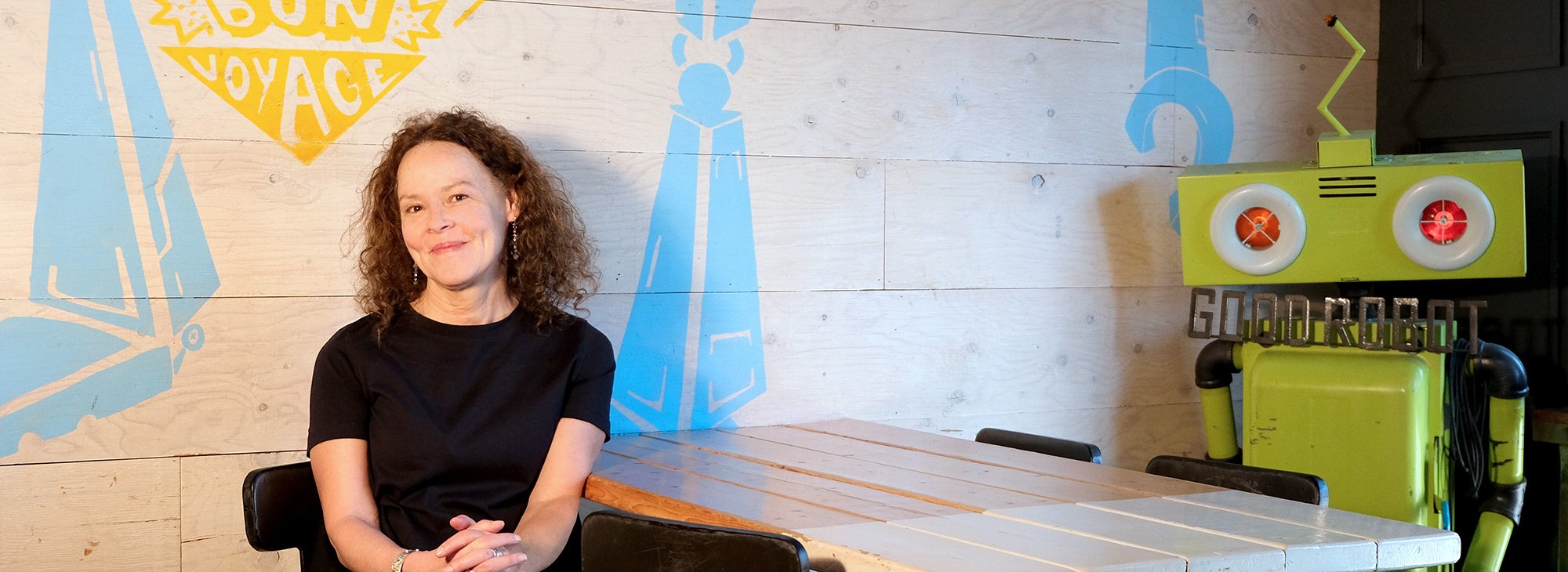
Dr. Danika van Proosdij
Saint Mary’s University is proud to share that Dr. Danika van Proosdij has been elected as one of the new Fellows by The Royal Society of Canada (RSC) and its members.
“Being elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada is an incredible honour. It should come as no surprise to anyone who has had the pleasure of working with Danika that her outstanding contributions to her field of research are being recognized,” says Dr. Adam Sarty, Associate Vice-President, Research, and Dean of the Faculty of Graduate Studies and Research at Saint Mary’s University.
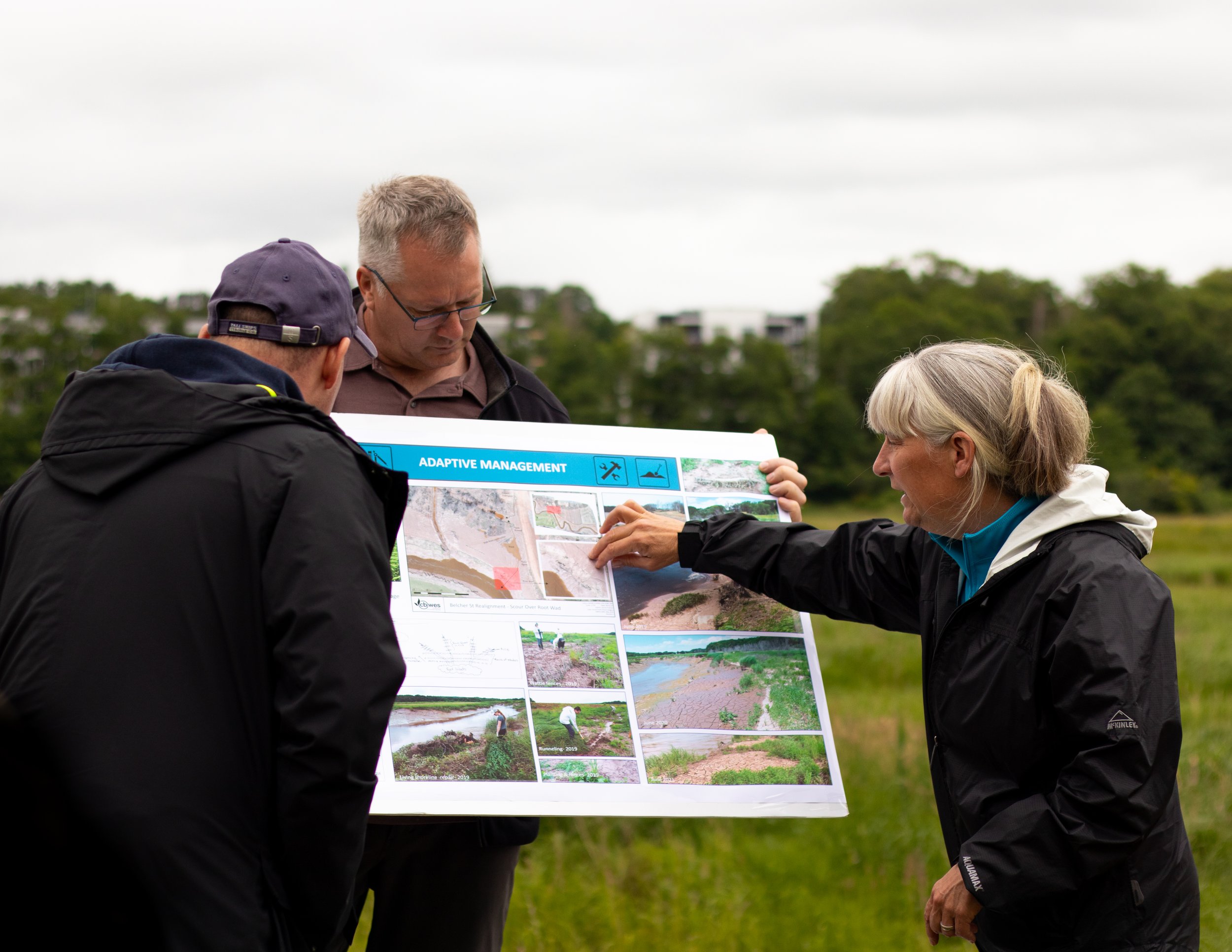
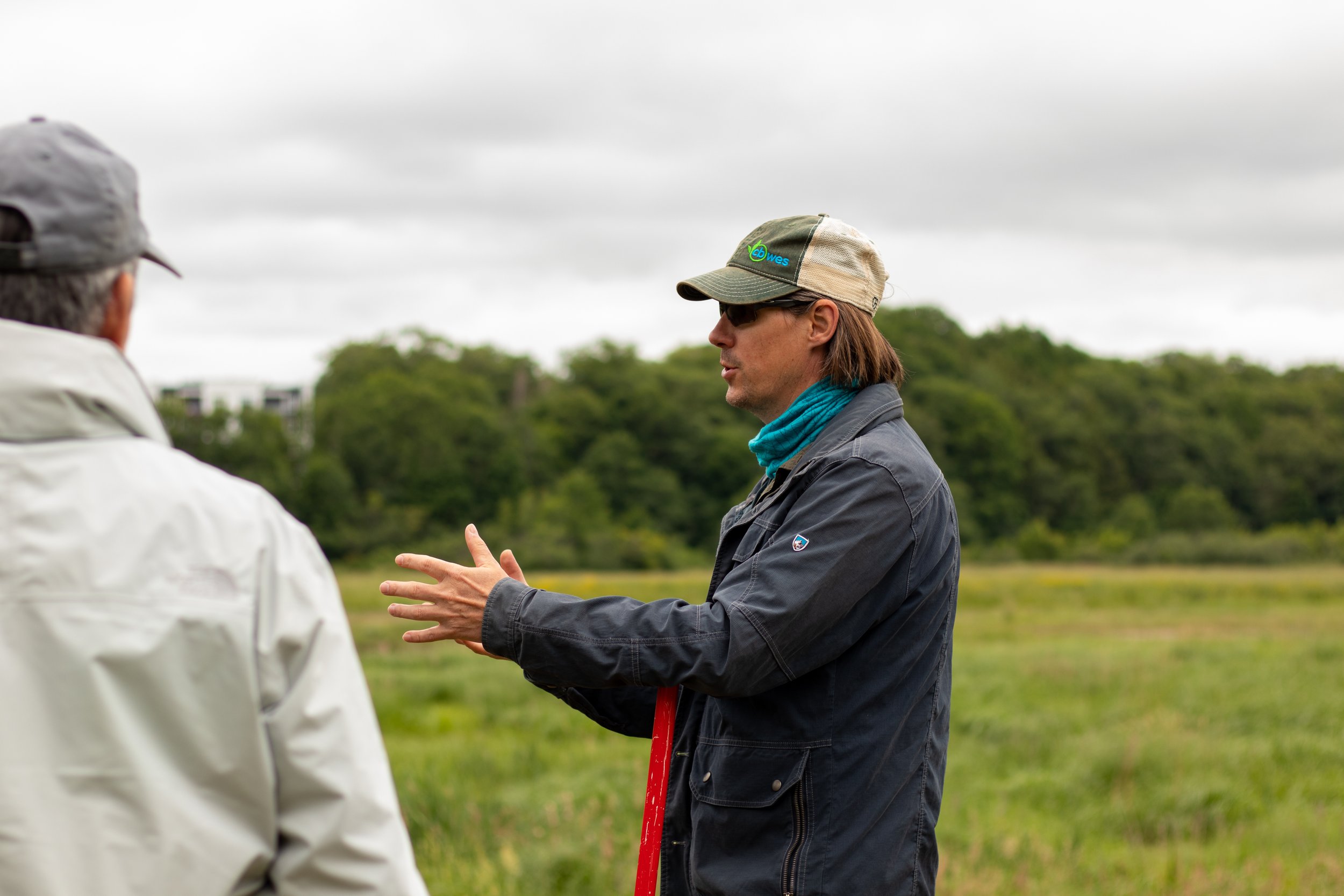
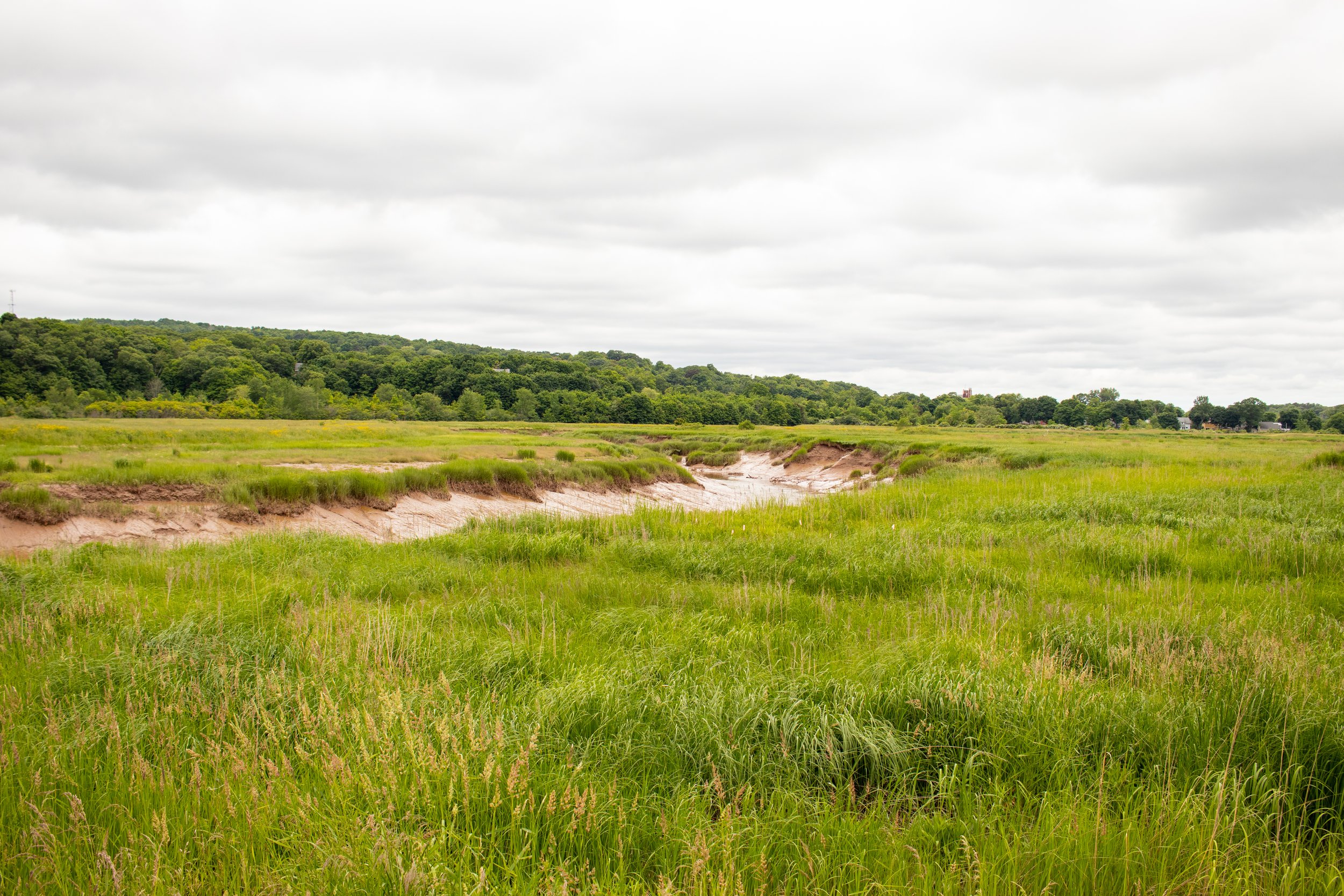
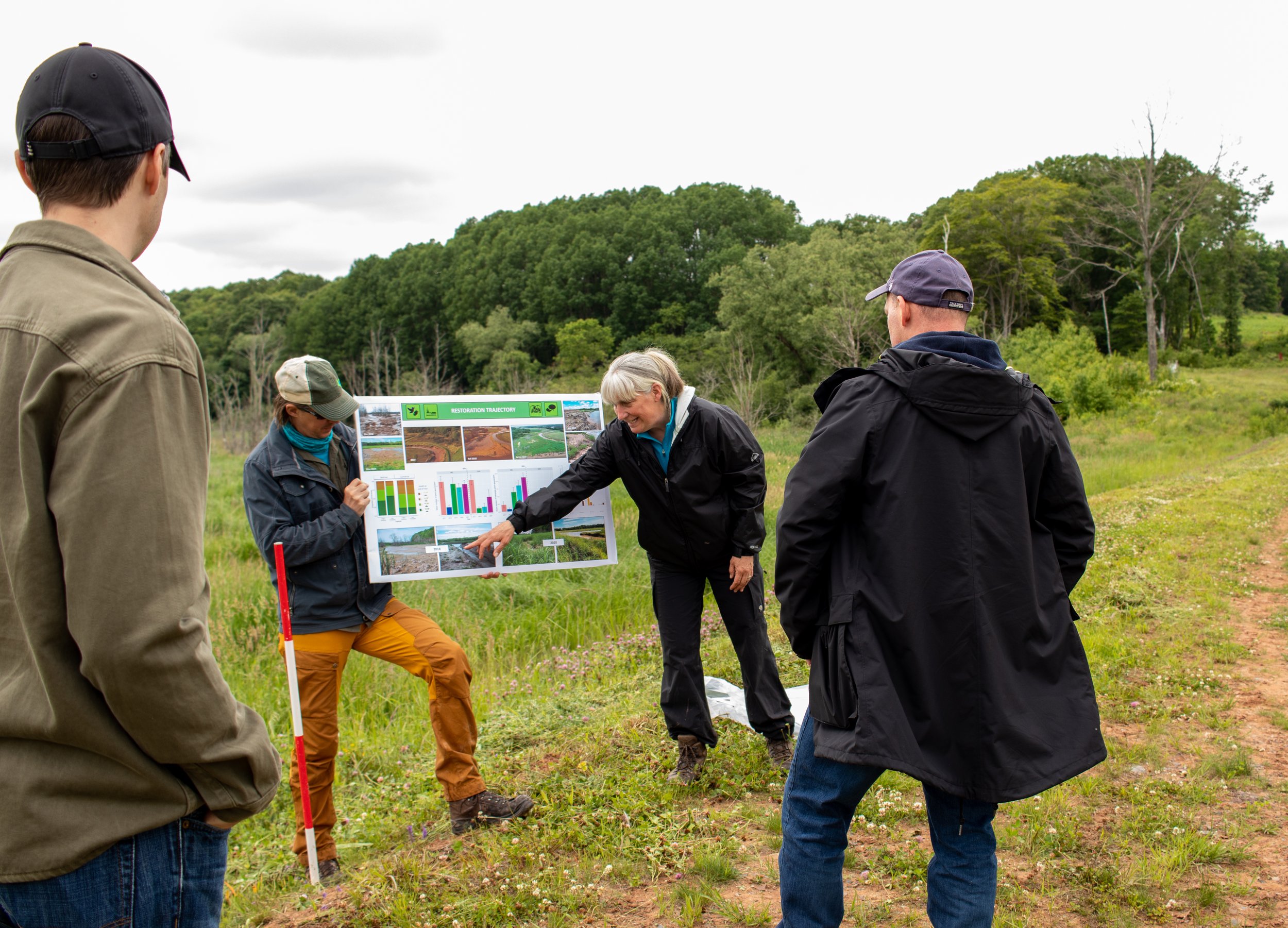
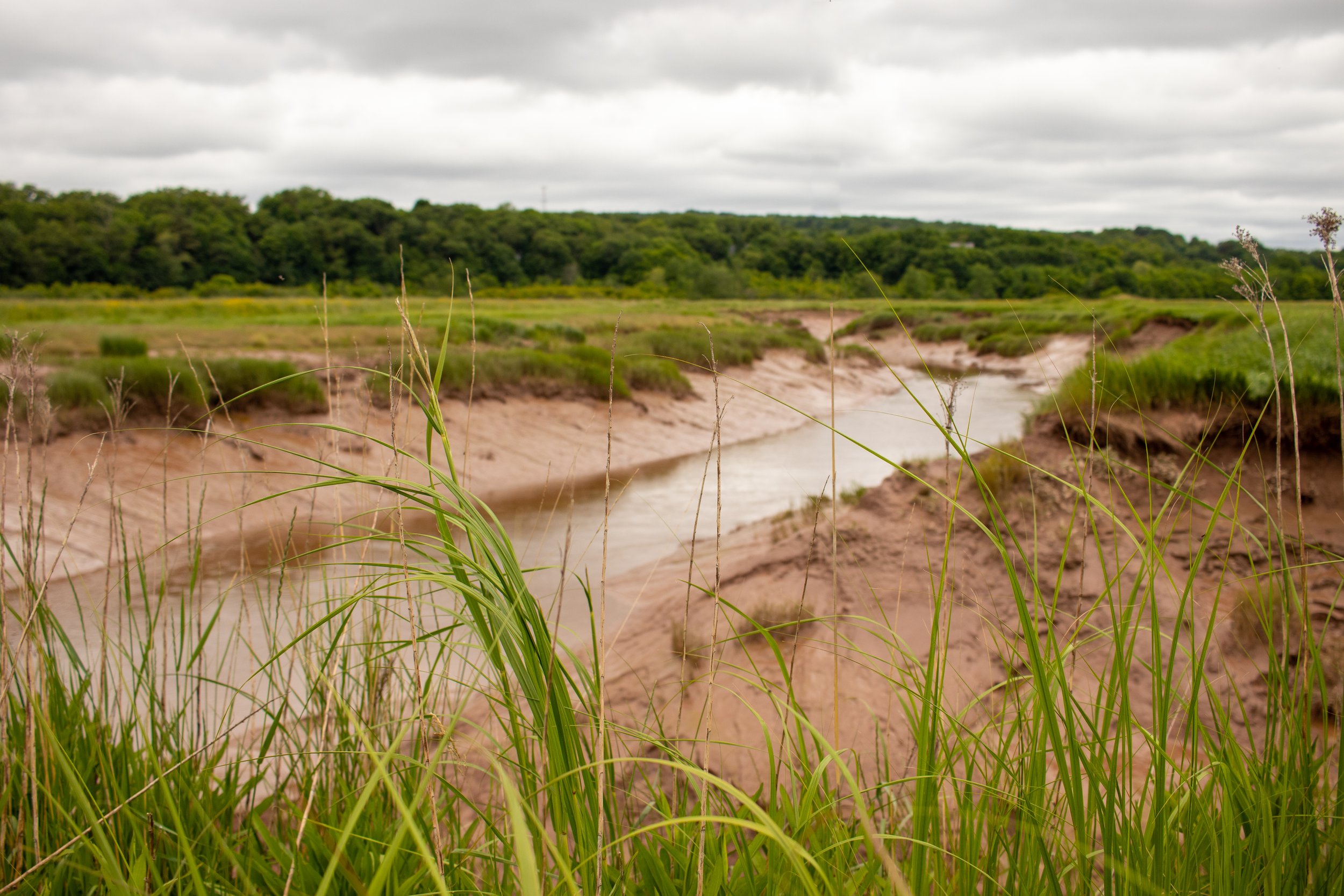
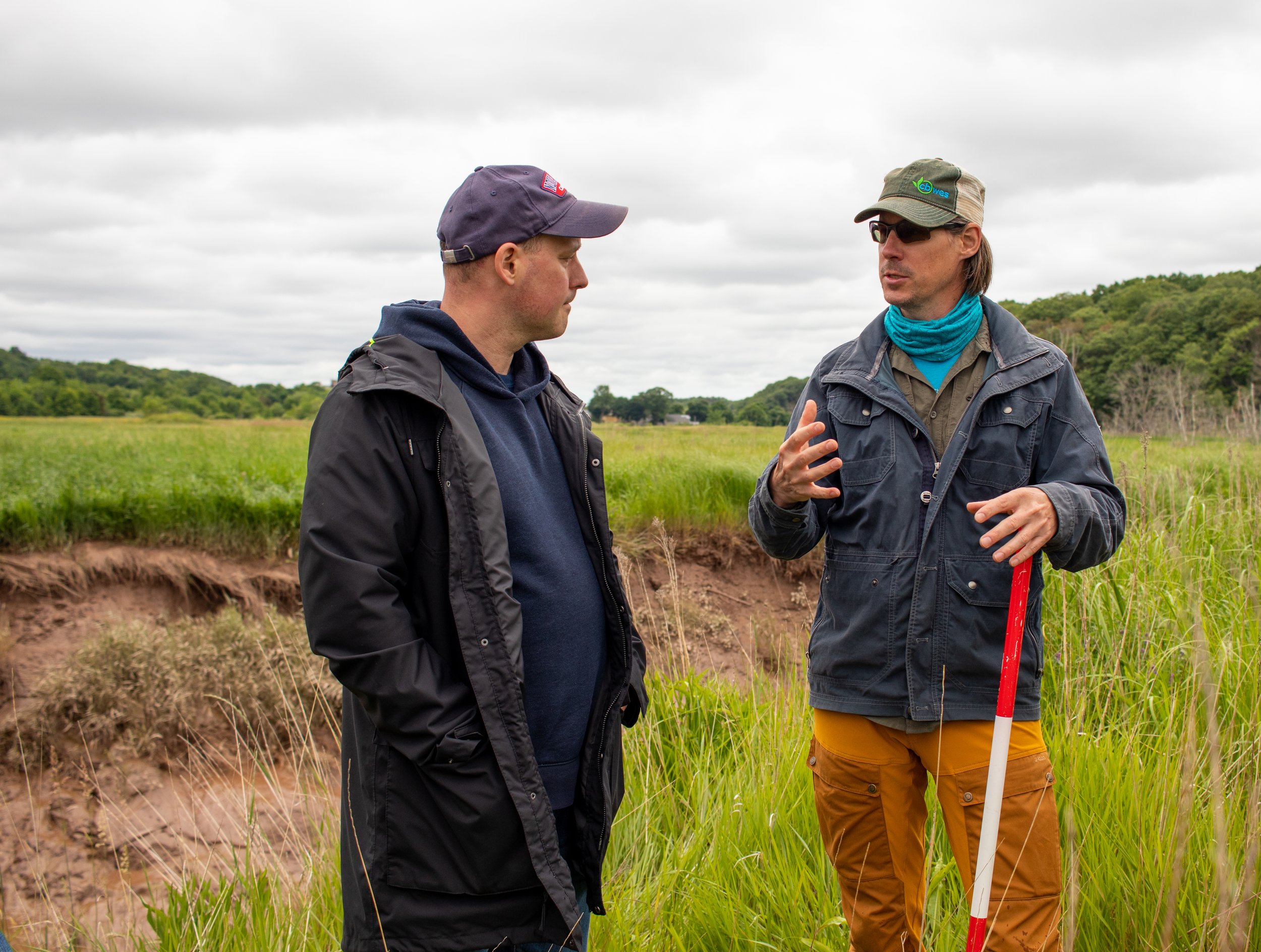
Dr. van Proosdij is the Director of TransCoastal Adaptations: Centre for Nature-Based Solutions and a professor with the Department of Geography and Environmental Studies at Saint Mary’s. Dr. van Proosdij is a Fellow of the Royal Canadian Geographical Society and is studying how coastal systems respond to natural and human drivers of change and is leveraging this understanding to integrate nature-based adaptation options in the protection of coastal communities. She has over 25 years of applied ecosystem-based coastal adaptation projects and vulnerability assessments in Canada and abroad.
One hundred and two new Fellows have been elected by their peers for their outstanding scholarly, scientific and artistic achievements. Recognition by the RSC for career achievement is the highest honour an individual can achieve in the Arts, Social Sciences and Sciences.
On Friday, November 25, 2022, the RSC will welcome the 2022 class of new Fellows and new Members of the RSC College and present awards for outstanding research and scholarly achievement. The ceremonies will be held in person in Calgary, Alberta.
Founded in 1882, the Royal Society of Canada (RSC) comprises the Academies of Arts, Humanities and Sciences and The College of New Scholars, Artists and Scientists. The RSC recognizes excellence, advises the government and the larger society, and promotes a culture of knowledge and innovation in Canada and with other national academies around the world.